Hernia
Hernias occur when an organ pushes through an opening in a muscle or tissue. They often occur in the abdomen but can also be found in the groin and upper thigh areas as well. Some people may have a hernia for years without any problems. However, hernias can also be painful and have serious complications, at which time surgery may be required. Typically, a bulge or lump will appear in the affected area. Sometimes it can be felt more when standing, rather than sitting, as there is more pressure on the abdominal muscles in an upright position.
The most common cause of hernias is a combination of strain and muscle weakness. Weakened areas in the abdominal wall are very susceptible places for intestines to push through, resulting in a hernia.
Hernia Types:
Inguinal Hernia
These are the most common type of hernias, found in the groin region, and happen when the intestines penetrate the inguinal canal. Although they occur in both males and females, they are more common in men.
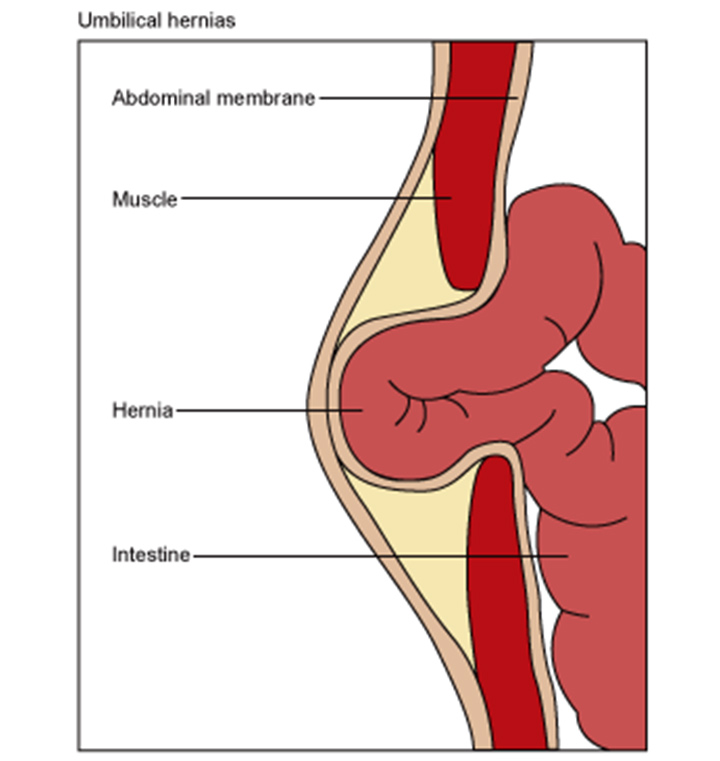
Umbilical Hernia
Umbilical hernias are the only kind of hernia that can go away by itself. They occur in children and are caused by intestines bulging through the abdominal wall near the navel (belly button). They usually go away on their own but occasionally they may need to be repaired surgically.
Incisional Hernia
Incisional hernias develop in weakened areas of the abdomen where a previous surgery has been performed. The tissues around an incision scar are weaker after surgery, which can allow the intestines to push through.
Hiatal Hernia
For additional information about this, please see our GERD/Hiatal Hernia page.
Treatment
The first step in hernia treatment is getting an official diagnosis. Often, a hernia can be felt externally. However, some hernias, including hiatal hernias, are not so obvious. Your primary care provider or gastroenterologist (a specialist that deals with diseases/conditions of the digestive system) can examine you and investigate the cause of your symptoms to determine if you have a hernia. Once a diagnosis is made you, or your provider, should call our office to discuss treatment options and/or surgical intervention.